 |
MAGISKA MOLEKYLERS WIKI |
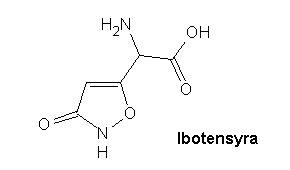
Ibotensyra
Generell information
Ibotensyra ├żr en vattenl├Čslig molekyl som ├żr naturligt f├Črekommande hos n├źgra arter i sl├żktet Amanita (flugsvampar), men har ├żven p├źtr├żffats i parasitsvampen Ophiocordyceps heteropoda som drabbar insekter i familjen Cicadoidea.[1]
Effekter
Ibotensyra har fler bieffekter ├żn muskimol (kraftigt illam├źende m.m.) och kan t.o.m anses vara giftig (neurotoxiska egenskaper n├żr den injicerats i hj├żrnan p├ź r├źttor[2]), en effekt som kan bero p├ź att den ├żr en NMDA-agonist, vilket leder till en ├Čverstimulerande effekt (exotoxicitet) n├żr det bildas ett ├Čverskott av calciumjoner. En konvertering till muskimol ├żr d├żrf├Čr ett m├źste f├Čr rekreationellt bruk!
| ŌĆ£ | Ibotenic acid evokes entheogenic effects in human beings at doses ranging from 50 - 100 mg (Chilton 1975; Theobald et al. 1968). An equivalent effect is produced by 10-15 mg of muscimol (Theobald et al. 1968; Waser 1967). After oral ingestion, the onset of the inebriation is rather slow, and generally 2-3 hours elapse before the full effects are felt (Chilton 1975). This delayed response has also been reported following ingestion of Amanita pantherina (Ott 1976a). The effects last for 6-8 hours, depending on dose. Effects are characterized by visual distortions, loss of equilibrium, mild muscle twitching (not convulsions, as has erroneously been reported), and altered auditory and visual perception (Chilton 1975; Ott 1976a). ŌĆö Ott (1993)[3] |
ŌĆØ |
Tillredning
En mindre m├żngd av molekylen dekarboxyleras i kroppen till den psykoaktiva alkaloiden muskimol. Detta f├Črklarar varf├Čr sibiriska flugsvampsanv├żndare l├żr ha druckit urin fr├źn renar som ├żtit r├Čd flugsvamp f├Čr att p├ź s├ź vis utnyttja svampens potens maximalt utan bieffekter.
Mer f├Črdelaktiga metoder f├Čr dekarboxylering ├żr torkning under l├źng tid eller uppv├żrmning (dock ej kokning d├ź det bryter ner molekylerna)[4]
En annan metod ├żr glutaminsyradekarboxylas (engelska glutamate decarboxylase/glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)[5]) som bl.a finns i citronjuice. Det ├żr ett enzym som normalt dekarboxylerar glutamat till GABA.
| ŌĆ£ | Additionally, a third sample, ŌĆ£GADŌĆØ as shown in FIG. 1, to a portion of undiluted filtrate added 14 mg of purified glutamate decarboxylase was added to 2 ml of fil trate. 0.3 mg of pyridoxal phosphate (P-5-P) was added, and the sample was maintained at 37 degrees Celsius for 2 hours. Then the sample was held at 37 degrees Celsius for another 2 hours then refrigerated. The resultant product resulted in a ratio of muscimol to ibotenic acid is displayed as "GADŌĆØ as shown in FIG. 1, which resulted in a ratio of 92.77 muscimol to ibotenic acid, as compared to the control sample of 0.29 muscimol to ibotenic acid. ŌĆö US Patent US20140004084A1[6] |
ŌĆØ |
Kemi
| Systematiskt namn | ╬▒-Amino-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-oxazoleacetic acid | |
| Trivialnamn | ibotensyra (sv), ibotenic acid (en) | |
| Kemisk formel | C5H6N2O4O | |
| Sm├żltpunkt | 151-152 C | |
| Kokpunkt | ||
| Molmassa | 158.11 g/mol | |
| Densitet | ||
| L├Čslighet | L├żs under extrahering |
Externa l├żnkar
- Ōåæ Unintentional ingestion of Cordyceps fungus-infected cicada nymphs causing ibotenic acid poisoning in Southern Vietnam. (Doan, 2017)
- Ōåæ Cholinergic lesions of the rat brain by ibotenic acid and 192 IgG-saporin: effects on somatostatin, substance P and neuropeptide Y levels in the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus (Nag, 1998)
- Ōåæ Ott., J (1993), Pharmacotheon: Entheogenic Drugs, Their Plant Sources and History, Chemistry and Effects of Entheogenic Amanita Species
- Ōåæ Amanita Notes by Michael S. Smith, Harvesting, Preparation and Effects of Amanita muscaria
- Ōåæ Wikipeia: Glutamate decarboxylase
- Ōåæ US Patent US20140004084A1: Method for producing muscimol and/or reducing ibotenic acid from amanita tissue